Introduction
As a blogger who often writes about health-related issues, I have come across many individuals who are affected by both glaucoma and depression. With the increasing prevalence of these conditions, many patients are looking for information on how their medications may impact their eye health. In this article, I will discuss the connection between Amitriptyline, a commonly prescribed antidepressant, and glaucoma, a leading cause of vision loss. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of what you need to know about Amitriptyline and glaucoma.
What is Amitriptyline?
Amitriptyline is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that has been around since the 1960s. It is primarily used to treat major depressive disorder, but it has also been prescribed for other conditions such as anxiety, neuropathic pain, and migraines. Amitriptyline works by increasing the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain, which helps to improve mood and alleviate pain. Although it is an effective medication for many individuals, it does come with some potential side effects, one of which is the possible exacerbation of glaucoma.
What is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve and can lead to irreversible vision loss if left untreated. The most common form of glaucoma is primary open-angle glaucoma, which occurs when the fluid drainage channels in the eye become blocked, leading to a buildup of pressure within the eye. This increased pressure can damage the optic nerve over time, resulting in vision loss. It is important to have regular eye exams to detect glaucoma early, as treatment can help to slow down or prevent further vision loss.
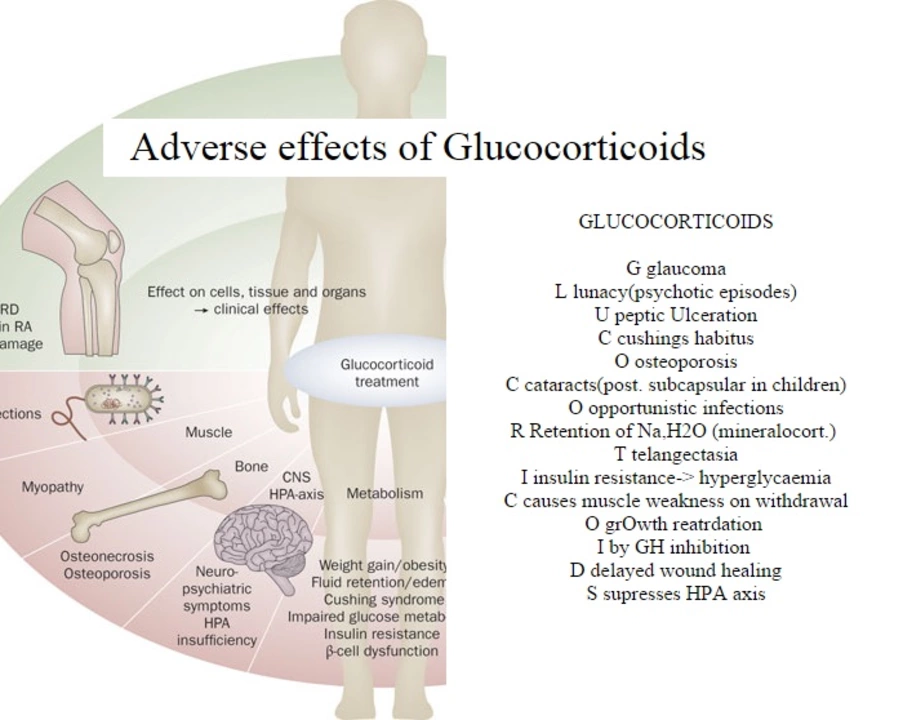
How Amitriptyline May Affect Glaucoma
Amitriptyline, like other tricyclic antidepressants, has been associated with an increased risk of developing angle-closure glaucoma, a less common but more severe form of the disease. Angle-closure glaucoma occurs when the iris (the colored part of the eye) blocks the drainage channels, causing a rapid rise in eye pressure. This condition is considered a medical emergency, as it can lead to permanent vision loss if not treated promptly.
Anticholinergic Effects
Amitriptyline's anticholinergic properties are believed to be responsible for its potential to exacerbate glaucoma. Anticholinergic medications can cause the muscles that control the size of the eye's pupil to relax, resulting in dilation. This can lead to the closure of the eye's drainage channels, especially in individuals who have a predisposition to angle-closure glaucoma. As a result, eye pressure may rise, potentially causing damage to the optic nerve.
Risk Factors and Precautions
While the risk of developing angle-closure glaucoma due to Amitriptyline use is relatively low, certain individuals may be more susceptible. Those with a family history of glaucoma, a personal history of angle-closure glaucoma, or narrow angles in their eyes are at a higher risk. If you fall into any of these categories, it is important to discuss the potential risks with your healthcare provider before starting Amitriptyline. They may recommend a thorough eye examination to assess your risk, and alternative medications may be considered if necessary.
Managing Glaucoma While on Amitriptyline
If you are currently taking Amitriptyline and have been diagnosed with glaucoma, there are steps you can take to manage your eye health. First and foremost, it is crucial to maintain regular appointments with your eye doctor to monitor your condition. They may also recommend additional treatments or adjustments to your medication regimen to help control your eye pressure.
Additionally, be sure to inform your healthcare provider of any changes in your vision or eye discomfort, as these could be signs of worsening glaucoma. Remember that early detection and intervention are key to preventing further vision loss.
Conclusion
While Amitriptyline has been an effective treatment for depression and other conditions for many individuals, it is essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with its use, including the exacerbation of glaucoma. By staying informed and maintaining open communication with your healthcare providers, you can help to ensure the best possible outcome for both your mental and eye health.






16 Comments
Jordan Corry May 5, 2023
This is life-changing info 🚨 I was on amitriptyline for years and never knew it could mess with my eyes. My grandma lost her vision because no one told her. Don't sleep on this. Your eyes are NOT replaceable.
Dan Gut May 6, 2023
The assertion that amitriptyline exacerbates angle-closure glaucoma is empirically unsupported in the majority of peer-reviewed literature. While anticholinergic effects are theoretically plausible, the incidence rate in clinical populations remains below 0.3%. The conflation of pharmacodynamic mechanisms with clinical outcomes is a common fallacy in lay medical discourse.
Mohamed Aseem May 7, 2023
LMAO you people actually believe this? My cousin took amitriptyline for 10 years and his eyesight got better. You're all just scared of big pharma. They don't want you to know the truth. The real cause is screen time and bad karma.
Paul Avratin May 9, 2023
The pharmacological interplay between tricyclic antidepressants and ocular dynamics reflects a complex neuromodulatory cascade. While the anticholinergic burden may induce pupillary dilation, the structural predisposition to narrow anterior chambers remains the primary determinant of angle-closure risk. Contextualizing pharmacovigilance data requires stratification by demographic, anatomical, and comorbid variables.
Brandi Busse May 9, 2023
Ive been on this med for 8 years and my eye pressure is fine so why are you all freaking out nobody ever told me this and now im scared but also kinda mad because if it was such a big deal why did my dr just give it to me without a warning
Colter Hettich May 10, 2023
Ah, yes-the modern medical-industrial complex, in its infinite wisdom, has once again reduced the human experience to a series of pharmacological variables... yet, in doing so, it forgets that the soul, too, has a physiology. Amitriptyline, in its quiet, tricyclic grace, does not merely alter neurotransmitters-it alters the *texture* of being. And if the eye’s pressure rises... perhaps it is the soul’s resistance to the weight of the world.
Prem Mukundan May 11, 2023
Bro, if you have narrow angles, you shouldn't even be on this med. Period. I'm a med student in Delhi and we get this drilled into us. Your doctor is either lazy or didn't do the basic exam. Get a gonioscopy. Stop scrolling and do something about your eyes.
Jensen Leong May 12, 2023
Thank you for sharing this critical information. 🙏 Early detection saves sight. I encourage everyone to consult with an ophthalmologist before initiating any anticholinergic regimen, especially if you have a family history of glaucoma. Your vision is irreplaceable.
Kelly McDonald May 13, 2023
This is the kind of post that makes me feel seen 💛 I’ve been on amitriptyline for my chronic pain and depression, and I’ve had glaucoma since I was 35. I’m so glad someone’s talking about this. I got my eyes checked every 6 months and my doc switched me to an SSRI after my last pressure spike. You’re not alone. Your mental health matters AND your eyes matter too.
Joe Gates May 15, 2023
I know this sounds like a stretch but hear me out-when you're depressed, you stop caring about your health. You skip eye appointments, forget your drops, and then your pressure spikes. Maybe it's not the amitriptyline causing the glaucoma-it's the depression making you ignore the signs. We need to treat the whole person, not just the symptoms. I’ve seen it too many times.
Tejas Manohar May 15, 2023
The clinical guidelines from the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) clearly recommend screening for narrow anterior chambers prior to initiating tricyclic antidepressants in patients over 50. Failure to adhere to this standard constitutes a breach of the standard of care. I urge all clinicians to implement pre-prescription gonioscopy.
Mohd Haroon May 15, 2023
The pharmacological mechanism is well-documented in the Journal of Clinical Neuroophthalmology, Vol. 41, Issue 2. The anticholinergic inhibition of the sphincter pupillae leads to relative pupillary block in predisposed individuals. This is not speculation-it is established pathophysiology. Dismissing it as anecdotal is dangerous.
harvey karlin May 16, 2023
Amitriptyline = ocular time bomb 🚫👁️ If you're on it and have a family history of glaucoma, you're playing Russian roulette with your vision. Swap it for something safer. Your brain won't die without it. Your eyes will.
Anil Bhadshah May 18, 2023
I'm a pharmacist in Mumbai and I always check for glaucoma risk before dispensing amitriptyline. If patient says 'my dad went blind' or 'I have headaches with bright lights'-I flag it immediately. Simple questions save sight. Don't wait for symptoms. Ask your doctor about gonioscopy.
Trupti B May 19, 2023
i took it for years and never had any problems so this is just fear mongering honestly i think people just wanna be dramatic about everything
lili riduan May 19, 2023
Thank you for writing this. I’m so glad someone finally said it out loud. I was terrified to tell my psychiatrist I was having eye pain because I didn’t want to seem like I was complaining. But I did-and they switched me. I cried. Not because I was sad-but because someone finally listened. You’re not alone. Your pain matters. Your vision matters. Keep speaking up 💛