Understanding Osteoporosis and Kidney Disease
Osteoporosis and kidney disease are two seemingly unrelated medical conditions. However, research has shown that there is a significant relationship between the two. In this article, we will explore the connection between osteoporosis and kidney disease, as well as the impact they have on one another. We will also discuss the symptoms, causes, and treatments for both conditions.
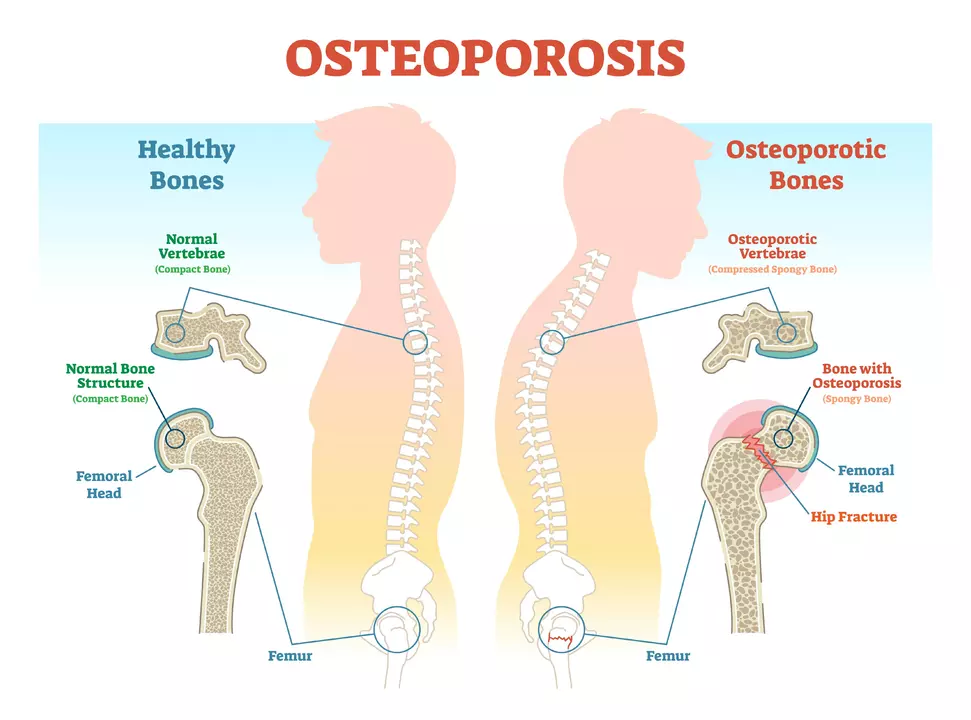
The Basics of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a medical condition in which the bones become weak and brittle. This happens due to a decrease in bone density, which can result in fractures and breaks. Osteoporosis is more common in older individuals, particularly postmenopausal women, but it can affect people of any age. Common risk factors for osteoporosis include age, gender, family history, and certain lifestyle factors such as smoking and a lack of physical activity.
There are often no symptoms of osteoporosis until a fracture occurs. However, some people may experience pain, a stooped posture, or a loss of height. Treatment for osteoporosis typically involves increasing bone density through medications, dietary changes, and exercise.
An Overview of Kidney Disease
Kidney disease, also known as renal disease, refers to any condition that impacts the kidneys' ability to effectively filter waste and excess fluid from the blood. Kidney disease can be acute or chronic, with chronic kidney disease (CKD) being the most common type. CKD is a progressive condition that can lead to kidney failure if left untreated.
Some common causes of kidney disease include diabetes, high blood pressure, and genetic factors. Symptoms of kidney disease can vary, but may include fatigue, changes in urine output, swelling, and nausea. Treatment for kidney disease often involves addressing the underlying cause and managing symptoms through medications, dietary changes, and dialysis if necessary.
How Osteoporosis and Kidney Disease Are Connected
Research has shown that individuals with chronic kidney disease are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis. This is due to several factors, including hormonal imbalances, decreased kidney function, and the buildup of waste products in the body. These factors can all contribute to a decrease in bone density, leading to the development of osteoporosis.
Additionally, certain medications used to treat kidney disease, such as corticosteroids, can increase the risk of osteoporosis by reducing bone density. This is especially true for individuals who require long-term treatment with these medications.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Osteoporosis in Kidney Disease Patients
It's important for individuals with kidney disease to be aware of the potential symptoms of osteoporosis, as early detection and treatment can help prevent fractures and other complications. Some common symptoms of osteoporosis in people with kidney disease include:
- Unexplained bone pain or tenderness
- Fractures that occur with minimal force or impact
- A decrease in height or a stooped posture
If you or someone you know with kidney disease experiences any of these symptoms, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and potential treatment options.
Preventing Osteoporosis in Kidney Disease Patients
There are several steps that individuals with kidney disease can take to help prevent the development of osteoporosis. Some of these preventative measures include:
- Maintaining a healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamin D
- Participating in regular weight-bearing exercises, such as walking or resistance training
- Quitting smoking, if applicable
- Limited alcohol consumption
- Working closely with healthcare professionals to manage kidney disease and any associated medications
By taking these steps, individuals with kidney disease can help to reduce their risk of developing osteoporosis and improve their overall health.
Treatment Options for Osteoporosis in Kidney Disease Patients
If an individual with kidney disease is diagnosed with osteoporosis, there are several treatment options available. These may include:
- Medications to increase bone density, such as bisphosphonates or hormone replacement therapy
- Calcium and vitamin D supplements
- Exercise programs specifically designed to improve bone health
It's important to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the best treatment plan for osteoporosis in individuals with kidney disease, as certain medications or therapies may need to be adjusted based on kidney function.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between osteoporosis and kidney disease is essential for individuals living with either condition. By recognizing the connection between the two, patients and healthcare professionals can work together to prevent, diagnose, and treat osteoporosis in those with kidney disease, ultimately improving their quality of life and overall health.







13 Comments
harvey karlin May 22, 2023
Yo, this is wild-kidney disease and osteoporosis are basically bone buddies in the shadows. When your kidneys tank, they stop activating vitamin D, and boom-your bones start throwing a tantrum. Corticosteroids? More like bone assassins. If you’re on dialysis, you’re basically playing Jenga with your skeleton.
Anil Bhadshah May 23, 2023
Very true! Calcium and vitamin D are non-negotiable for CKD patients, but dosage matters-too much can cause calcification. Always work with a nephrologist and a dietitian. 💪🩺
lili riduan May 25, 2023
I had a cousin on dialysis who broke her wrist just sneezing… it broke my heart. This article should be mandatory reading for every nephrology clinic. Thank you for writing this-so many people don’t know this link exists.
Dilip p May 26, 2023
The physiological interplay here is elegant in its tragedy. The kidneys regulate phosphate, calcium, and PTH-when they fail, the bone remodeling cycle becomes a feedback loop of decay. It’s not merely a comorbidity; it’s a systemic cascade. We must treat the kidneys to save the skeleton.
Trupti B May 27, 2023
so like… if your kidneys are bad your bones just crumble?? like fr??
Tejas Manohar May 29, 2023
While the physiological mechanisms are well-documented, the clinical implications demand a paradigm shift in patient education. Prophylactic bone density screening should be integrated into routine CKD management protocols, not treated as an afterthought. This is not merely a correlation-it is a clinical imperative.
ANTHONY MOORE May 30, 2023
My dad’s on dialysis and he walks every morning. No fancy gear, just sneakers and a cane. Said it’s the only thing keeping him from turning into a human question mark. Small wins, right?
VEER Design May 31, 2023
Imagine your kidneys are the orchestra conductor… and when they quit, the bone cells start playing jazz without a rhythm. Calcium? Vitamin D? They’re just confused musicians trying to find their sheet music. 🎻💀
Vivian Chan June 2, 2023
Did you know the pharmaceutical industry knows this connection? That’s why bisphosphonates are pushed so hard on CKD patients-because they profit from bone fractures. The real solution? Stop poisoning kidneys with processed food and sodium. But they won’t tell you that.
Kathleen Root-Bunten June 3, 2023
Interesting! I wonder if there’s data on whether plant-based diets help or hurt bone density in CKD? I’ve heard conflicting things about oxalates and phosphorus. Would love to see a follow-up on dietary nuances.
andrew garcia June 3, 2023
It's humbling to realize how deeply our organs rely on one another. A failing kidney doesn't just stop filtering-it unravels the body's balance in ways we're still learning. Thank you for shedding light on this silent connection. 🙏
Mohd Haroon June 3, 2023
One must not overlook the epistemological dimension: if osteoporosis is the visible symptom, then chronic kidney disease is the ontological root. To treat the bone without healing the kidney is to polish the coffin while the soul still breathes. The medical paradigm must evolve from compartmentalization to holism.
Leslie Ezelle June 5, 2023
Ugh, I’ve seen this too many times. Doctors treat the kidney like it’s the only thing that matters. Meanwhile, the patient’s spine collapses from osteoporosis and no one connects the dots. It’s negligence dressed in white coats. Someone needs to audit this.