Syphilis Progression: Stages, Symptoms, and What Happens If It’s Left Untreated
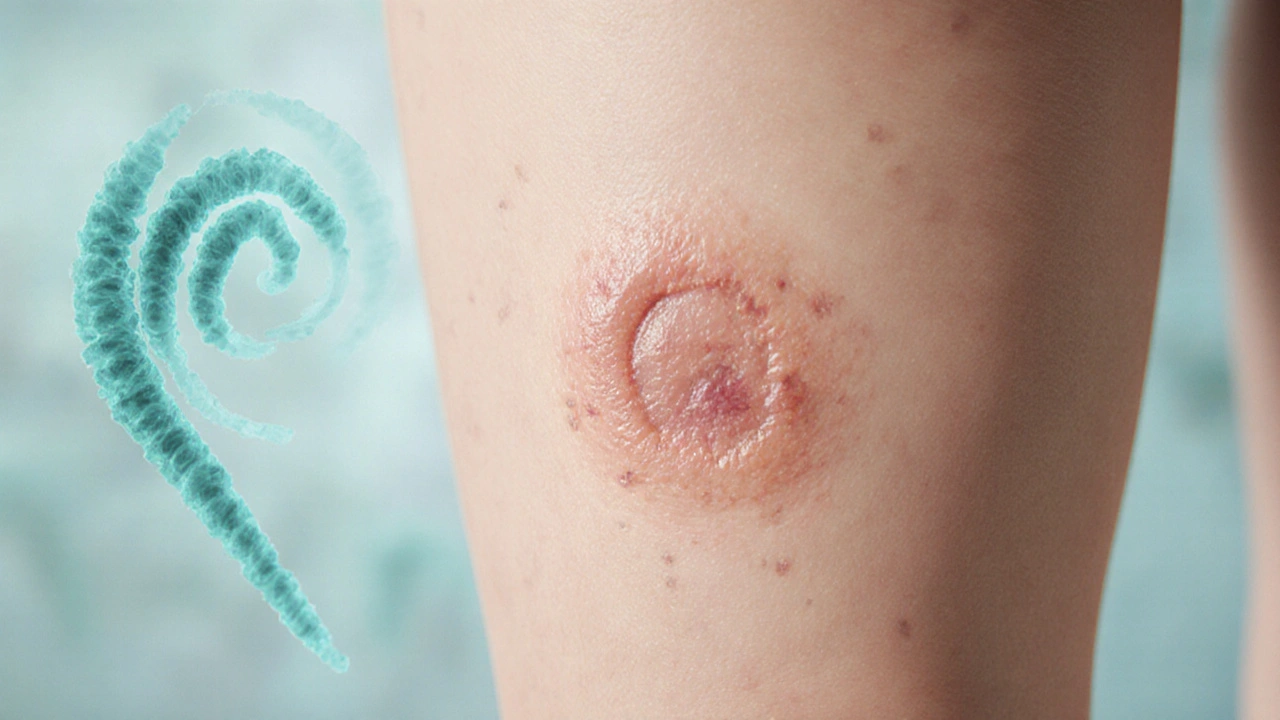
When syphilis, a bacterial infection caused by Treponema pallidum that spreads primarily through sexual contact. Also known as the great imitator, it can look like many other conditions and quietly damage organs over years. goes untreated, it doesn’t just stick around—it evolves. Syphilis progression happens in clear stages, and each one brings new risks. Many people don’t realize they have it because the early signs are easy to miss, like a single sore that heals on its own. But that doesn’t mean the infection is gone.
After the first sore fades, secondary syphilis, a widespread reaction that includes rashes, fever, and swollen lymph nodes often appears weeks later. This stage is highly contagious and can come and go. People might think it’s the flu or a skin allergy, so they skip testing. But if it’s not caught here, the infection slips into latent syphilis, a silent phase where no symptoms show up but the bacteria are still active in the body. This can last for years—sometimes decades—without anyone knowing.
Then comes the danger zone: tertiary syphilis, the late stage that attacks the heart, brain, nerves, bones, and other organs. At this point, damage can be irreversible. Neurosyphilis can cause dementia, blindness, or paralysis. Cardiovascular syphilis can lead to aneurysms or heart failure. These aren’t rare outcomes—they’re well-documented consequences of delayed treatment. The CDC reports that even today, late-stage syphilis still shows up in people who avoided testing or didn’t follow through with care.
What makes syphilis progression so dangerous isn’t just how it spreads—it’s how quietly it works. A person can feel fine for years while the infection quietly destroys tissue. That’s why testing matters, even if you feel healthy. If you’ve had unprotected sex, shared needles, or had a partner diagnosed with syphilis, getting tested is the only way to know. Blood tests are simple, fast, and accurate.
Good news: syphilis is curable. Antibiotics, especially penicillin, work extremely well if caught early. Even in later stages, treatment can stop further damage. But it can’t undo what’s already been done. That’s why timing is everything. The sooner you act, the less risk you face.
The posts below dive into real cases, treatment protocols, and how syphilis interacts with other health conditions like HIV and pregnancy. You’ll find clear breakdowns of symptoms at each stage, what doctors look for, and why skipping treatment is never worth the risk. Whether you’re concerned about your own health or just trying to understand how this infection works, these guides give you the facts without the fluff.
- Archer Pennington
- 17
Syphilis Stages Explained: From Primary to Tertiary
Learn the four stages of syphilis, their symptoms, diagnosis methods, and treatment options. Get clear guidance on prevention, early detection, and when to seek medical care.
Read more